Marcin Stolarski PhD Just another rocket scientist
Projects
2004 – 2006
SSETI ESEO – The European Student Earth Orbiter.

SSETI ESEO is the second ESA student satellite, following 2005’s SSETI Express. ESEO is also a technical precursor to the SSETI ESMO micro-satellite and will test hardware in a hard-radiation environment for future SSETI exploration missions beyond Earth’s orbit.
Following the successful model of SSETI Express, the satellite platform of ESEO is being developed by student teams across Europe. Each team is dedicated to particular subsystems, such as the on-board computer, the propulsion system, the communications antennas, etc. The ESEO platform will carry a number of interesting payloads to achieve its objectives.
Functions:
– On Board Data Handling System (hardware and software): developer.
2004 – 2004
FTTL – Fault Tolerance Templates Library.
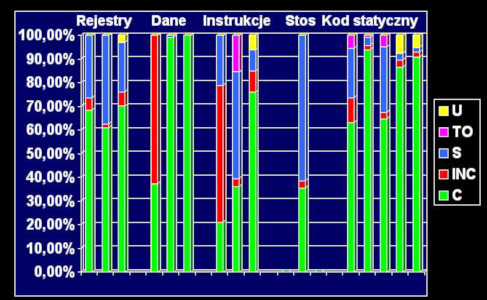
The mechanism of improving system stability consist in a tripled redundancy of data and calculations. FTTL is special library of variables, which implies tripling data and calculations made on that data.
Functions:
– System design: manager, developer.
2004 – 2006
VirtualCAN

VirtualCAN allows testing of the satellite’s apparatus and software during the construction stage of the prototype. Its main advantage is the fact of using the Internet as a way of communication to test the components when they are in there parent laboratories all over the world.
Functions:
– System design: manager, developer.
2004 – 2011
BOBAS – Build Occasionally Balloon Attached Satellite (high altitude balloons missions).

BOBAS are several stratospheric balloon missions for testing electronic equipment for project like SSETI ESEO, PW-SAT, YES2 or DGSS (Distributed Ground Station System).
Functions:
– Board electronic: manager, developer.
– Ground Station: manager, developer.
– Missions: manager.
2006 – 2007
YES2 – Young Engineers’ Satellite 2.

The Young Engineers’ Satellite 2 (YES2) is a 36 kg student-built tether satellite that is part of ESA’s Foton-M3 microgravity mission. The launch of the Russian Foton-M3 occurred on September 14, 2007 at 13:00 (CEST) by a Soyuz-U launcher. The project was carried out by Delta-Utec SRC and supervised by the ESA Education Office and was nearly entirely designed and build by students and young engineers.
The YES2 deployment took place Sept. 25, 2007. The mission objective was to deploy a 30 km long and 0.5 mm thin tether (made of Dyneema) in two controlled stages, in order to release a small, spherical, lightweight reentry capsule called Fotino into a predetermined trajectory to a landing area in Kazakhstan.
Functions:
– Mobile ground station: manager, developer.
– Recovery mission: manager, operator of the mobile ground station.
– Communication systems (antennas and transceivers): consultant.
– GPS system: consultant.
2006 – 2009
DGSS – Distributed Ground Station System
DGSS is based on parallel reception of data from satellite by a number of ground stations and subsequent comparison of this data in the computer system. According to the very definition, if reception errors in ground stations are independent of each other, the probability of receiving an error-free packet increases together with the number of ground stations.
Functions:
– System design: manager, developer.
2006 – 2009
GENSO – Global Educational Network for Satellite Operations.

The Global Educational Network for Satellite Operations (GENSO) is forming by a worldwide network of ground stations and spacecraft which can interact via a software standard. The GENSO aims to increase the return from educational space missions and changed the way that these missions are managed, dramatically increasing the level of access to orbital educational spacecraft.
Functions:
– Communication system: consultant.
2007 – 2009
PW-SAT – First Polish Student Satellite.
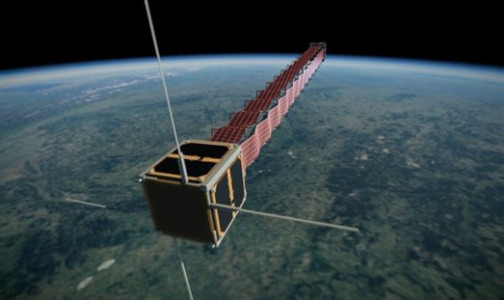
PW-Sat is the first Polish artificial satellite which was launched 13 February 2012 from ELA-1 at Guiana Space Centre aboard Italian-built Vega launch vehicle during its maiden voyage. Its mission was to test experimental elastic solar cells, as well as an orbital decay technology consisting of a “tail” designed to speed re-entry. It was expected to last for 1 year.
PW-Sat was a type of CubeSat satellite and it was constructed by the Faculty of Power and Aeronautical Engineering of Warsaw University of Technology, in cooperation with the Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences, and is the first Polish satellite.
Functions:
– Communication system: manager, developer.
– Ground station system: manager, developer.
– Distributed Ground Station System experiment: manager.
– System design: manager, developer.
2009 – 2009
PTF – Precise Timing Facility for Galileo Project.

The Precise Timing Facility (PTF) is considered as a key element of the Ground Mission Segment (GMS) in the Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). The PTF major purpose is to generate the physical time scale of Galileo, the Galileo System Time (GST) with two main functions: the provision of a very stable time reference for navigation purposes and the metrological timekeeping.
Functions:
– Network communication system: developer.
2009 – 2011
SPEKTROP – opto-electronic platform for fast multi-spectral imaging.
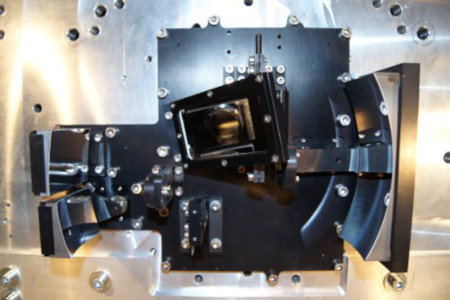
SPEKTROP is opto-electronic platform for fast multi-spectral (from 0,35µm up to 20µm) imaging in harsh environmental conditions. System use anti-vibration platform for optical head used in aircrafts and fast data collection system.
Functions:
– Software: developer.
2011 – 2012
RecAv – Reconfigurable Avionic.
RecAv is study about the potential use of reconfigurable FPGAs in the context of Fault Tolerance Computers and digital systems for space systems.
Functions:
– Project: manager
– System: developer.
2011 – 2014
BRITE-PL – Bright Target Explorer (first polish scientific satellite).

Bright Target Explorer or BRITE, also known as Canadian Advanced Nanospace eXperiment 3 (CanX-3) is a constellation of six nanosatellites operated by a consortium of universities from Canada, Austria and Poland.
The BRITE satellites were designed by the Institute for Aerospace Studies at the University of Toronto under the Canadian Advanced Nanospace eXperiment Program. The satellites is built around the Generic Nanosatellite Bus, a cube-shaped spacecraft with sides of 20 centimetres (7.9 in) which was first used in current BRITE version for the satellite CanX-3. One satellite is called BRITE-Toronto while the other is called BRITE-Montreal.
The satellite is intended for astro-photometry of the brightest stars in single wavelength band. UniBRITE-1, BRITE-Toronto and Heweliusz BRITE-PL photometers are sensitive to the red light, while BRITE-Montreal, Lem BRITE-PL and BRITE-AUSTRIA are sensitive to the blue light.
Functions:
– Communication system: manager, tester.
– Ground Station: manager, developer.
2011 – Present
Marcin Stolarski YouTube channel.

Marcin Stolarski YouTube channel is internet TV with popular science movies. It has series like BRITE-TV about BRITE constellation satellites, MARLAB about other project and interesting places or zRozum (understood) about how something works.
Functions:
– Presenter, executive producer.
2012 – 2013
InSide – In door localization system using VLF.

InSide project is system for mobile object localization in hostile environment for radio waves (buildings, underwater, underground). It use VLF beacon stations for transmit radio wave localization grid.
Functions:
– Project: manager
– System: developer.
2012 – 2013
PAS – Pilot Assist for Ships – System for Navigation in Harbours.

Pilot Assist for Ships is system for large ships coming to harbour. Such a system should fulfil legal rights and should be possible to extend its functionality in time.
Functions:
– Communication system: consultant.
2012 – 2014
Assert System – radar system for asteroids.
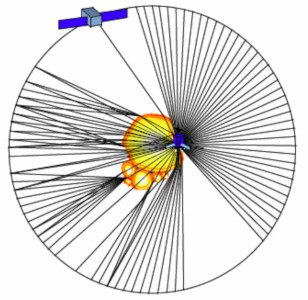
Assert System is radar system for asteroid’s (or comet) scanner using frequency about 60 MHz. It bases on two modules. One named “Lander” is module placed on asteroid, second named “Satellite” flown around the asteroid. Lander and Satellite have two-direction communication channel. Quality of this channel depends on RF attenuation signal transmitted through the asteroid.
Functions:
– RF front-end: manager, developer.
2013 – 2014
STIX – The Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays for Solar Orbiter.
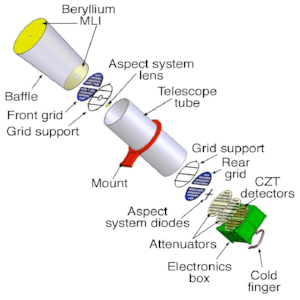
The Spectrometer/Telescope for Imaging X-rays (STIX) is one of the 10 instruments that are part of the scientific payload for the ESA Solar Orbiter Mission. The STIX instrument is an X-ray imager whose purpose is to study the extremely hot solar plasma and flare-accelerated high-energy electrons accelerated. It can detect solar X-rays from 4 to 150 keV.
Functions:
– Electronic board: co-manager
– Aspect system board: developer.
2013 – 2013
FameLab

FameLab was set up in 2005 by Cheltenham Science Festival in partnership with NESTA. In Famelab, contestants give short (maximum three minute) presentations unaided by slides on an area of science, technology, engineering or mathematics (STEM) that they have been researching. They aim to give their presentation in a way that engages the general public, not simply scientists etc. who already have technical or specific knowledge on the area. This point is taken into account by the judging panel, usually science communicators themselves, who assess the communicators on clarity, content and communication before deciding who to put through to the next round of competition. Famelab has regional heats in its participating countries, followed by national finals and then the international finals taking place every year at Cheltenham Science Festival.
Functions:
– Presenter.
2013 – 2015
SACC – Satellite Adaptive Communication Cannel.

The aim of the SACC project realized for European Space Agency (ESA) is to realize a model of adaptive communication system for small satellite in low Earth orbit (LEO). The data generated by the satellite payload have to be transmitted to the ground station (GS). But when LEO satellite is used, the satellite is visible from the GS only during short time of the orbiting period, thus only limited amount of the data can be received by the GS. To increase the total amount of the received data, adaptive communications system is proposed to use. Depending on the distance between the satellite and the GS and the radio link quality during the satellite passage over the GS, the data from the satellite will be transmitted with adaptively changed parameters in order to maximize total amount of the sent data. To realize such system a return channel from the GS to the satellite is necessary, to send an information about quality of the received signal. If the quality of the signal is good, the speed of the transmission from the satellite can be increased.
Functions:
– Project: manager.
– System: developer.
2013 – 2015
Pan Stanislaw (Mr. Stanislaw).

Pan Stanislaw (Mr. Stanislaw) is educational project in primary school where child prepare elements for cubesat satellite mission.
Functions:
– Lecturer, co-manager.
2013 – 2015
Uniwesytet Dzieci (Child’s University).

Uniwesytet Dzieci (Child’s University) is educational project where professional engineers and university lectures have meeting/lectures with primary school child.
Functions:
– Lecturer.
2013 - 2019
ERC – European Rover Challenge.

European Rover Challenge is the biggest space and robotics openair event in Europe. The event is addressed to a wide audience: adolescents, adults and families with children. Event consists of European Rover Challenge Zone and Science-Technology Exhibition Zone. In the Challenge Zone there will be a special track where will be held a competition of Martian rovers. Participants are students, graduates and university staff. The task facing teams is to design and build a Martian rover, which obtains the highest score in five competitions. In the Science-Technology Exhibitions’ Zone there will be prepared outdoor shows popularizing science and new technology, aimed at people of all ages. For two days visitors will able to take part in real science festival, watch experiments, participate in workshops and presentations, which will vary in terms of age and interest of the audience. For visitors provides numerous activities and competitions.
Functions:
– RF systems: co-manager, judge.
2013 – 2016
BikeMic – Bicycle microphone.

BikeMic or microphone for bicycles is a device that you connect in between your headphones and music player (like smartphone). In order to do that you just plug BikeMic cable to headphone jack of your player and headphones cable into BikeMic output. From now on, music from your player is feed into BikeMic. BikeMic has a built-in stereo microphone which record sound of your surroundings and then mixes them with your music in order you are able to listen to both of them simultaneously.
Functions:
– Project: manager.
– System: developer.
2014 – 2015
AstroBot.

AstroBot is competition for primary school child in subject like Lego Mindstorms robotics and space knowledge.
Functions:
– Lecturer, judge.
2014 – 2014
SRS – Satellite Radio Simulator.

SRS is satellite and ground equipment RF systems simulator for test RF compatibility. It generate real RF signals which can be received by satellites and ground stations. System based on Software Defined Technology and was use for testing BRITE-PL satellites and BRITE-PL ground station.
Functions:
– Project: manager
– System: developer.
2015 – 2015
Potyczki Naukowców (Skirmish Scientists) – PLANETE+ TV popular science program.

Potyczki Naukowców (Skirmish Scientists) is popular science TV program developed for channel PLANETE+. Four presenters, who are professional scientists or engineers presents his view on episode subject like telecommunications.
Functions:
– TV Presenter.
2015 – Present
CANduino – The Arduino CANsat project.

CANduino is a CANsat platform which is designed according to requirements of ESA EUROPEAN CANSAT COMPETITION (ECS). It uses electronic components in Arduino standard. It is a platform intended to help in building your own CANsat. It consists of ABS plastic structure and Arduino electronics. It is important that it does not need any sophisticated PCBs because it utilizes Arduino standard peripherals which are available in almost every shop for electronics hobbyists. Additionally, CANduino kits do not require any specialist tools to be assembled. It is enough to have knife, tweezers, screwdriver and PC computer to program the kit.
Functions:
– Project: manager
– System: developer.
2015 – 2015
GNSSW – GNS Receiver for Space Applications.
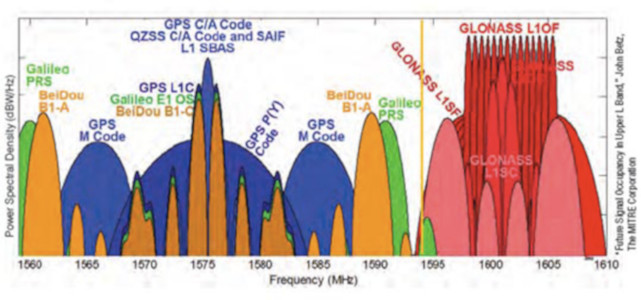
GNSSW Receiver Project target is to develop and test easily reconfigurable pure SW receiver for space applications.
Functions:
– RF front-end: manager, developer.
2015 – 2016
PSIK – Polska Szkola Inzynierii kosmicznej (Polish Space Engineering School)

PSIK is educational project for primary and secondary school students. It is training and competition in building CANsat project. It is opportunity to connect professionals space engineers with students and preparing semi space project using the CANduino’s kits.
Functions:
– Lecturer, manager.
2016 - 2019
NSC – Near Space Conference

NSC is conference in Poland for people who develop or interest Near Space Project like stratospheric balloons but not only. It is open for any close project like student’s cubesats or UAVs.
Functions:
– Lecturer, panel chairman.
2016
Airborne Wind Energy at Ampyx Power

Globally the demand for energy increases. Ampyx Power has the ambition to meet this demand at the lowest cost and in a sustainable way. We develop Airborne Wind Energy systems that convert wind at higher altitudes into electricity; a cost efficient technology using an abundant natural resource.
Functions:
– Communication systems (antennas and transceivers): consultant.
2016 - 2019
SAT-AIS-PL satellite
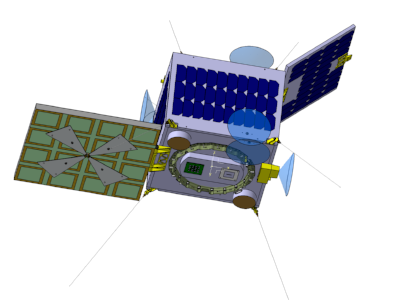
SAT-AIS-PL is a satellite system for monitoring maritime traffic. System will collect information from the automatic identification system (AIS) for security and administration of maritime traffic. Transmission of data from ships into the ground stations will be upgraded with a new standard VDES, to be introduced by the International Telecommunication Union in the coming years. Satellite SAT-AIS-PL will be the first Polish satellite industry, whose performance was commissioned a consortium of industrial and scientific chaired Creotech Instruments SA, in accordance with the standards in force in the European Space Agency.
Functions:
– RF systems (ground and flight) manager.
2016 - 2019
SAR satellite
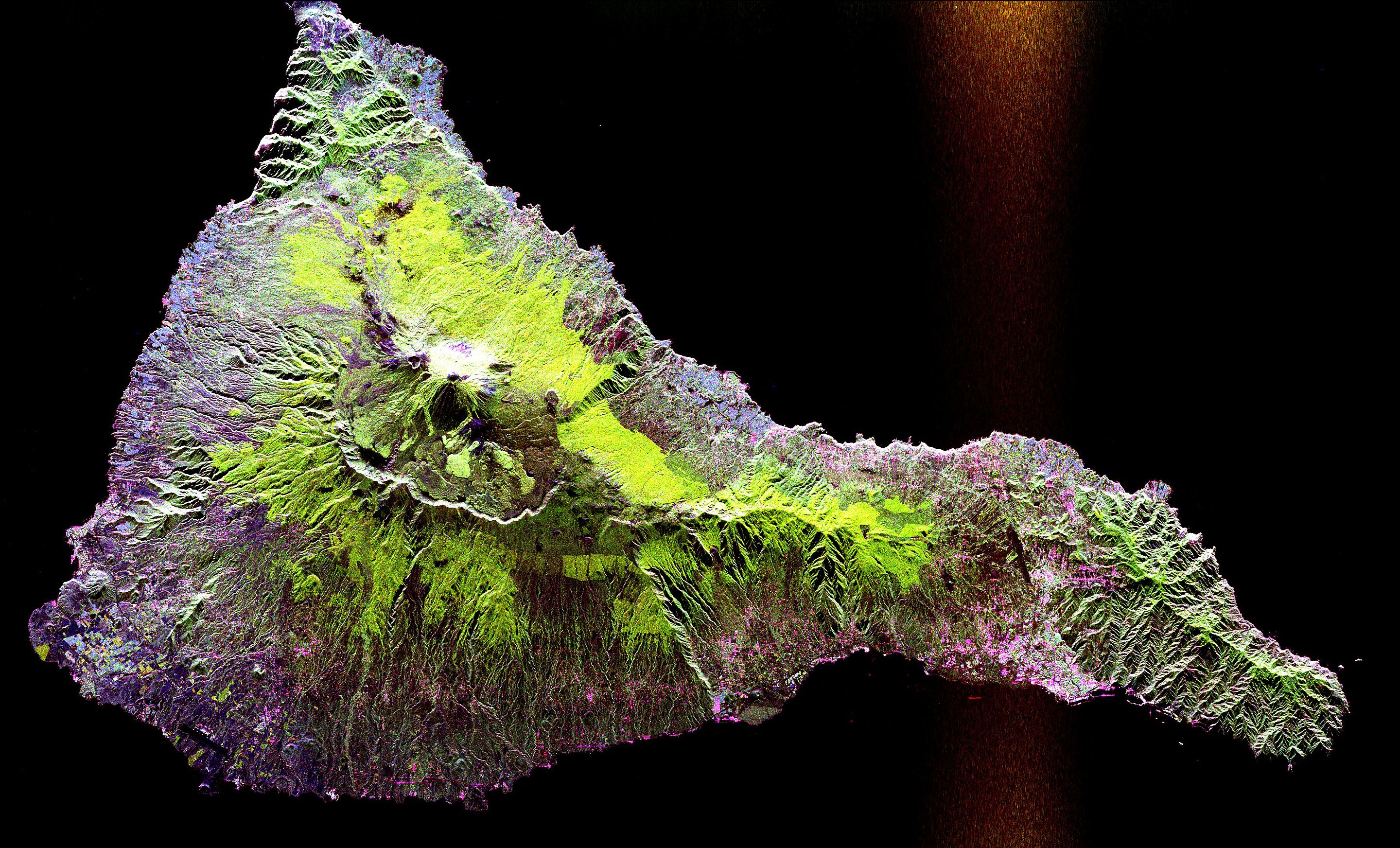
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes.[1] SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target in the time taken for the radar pulses to return to the antenna creates the large synthetic antenna aperture (the size of the antenna). Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical (a large antenna) or synthetic (a moving antenna) – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas.
Functions:
– Systems and test consultant
2016 - 2019
HyperSat satellite platform
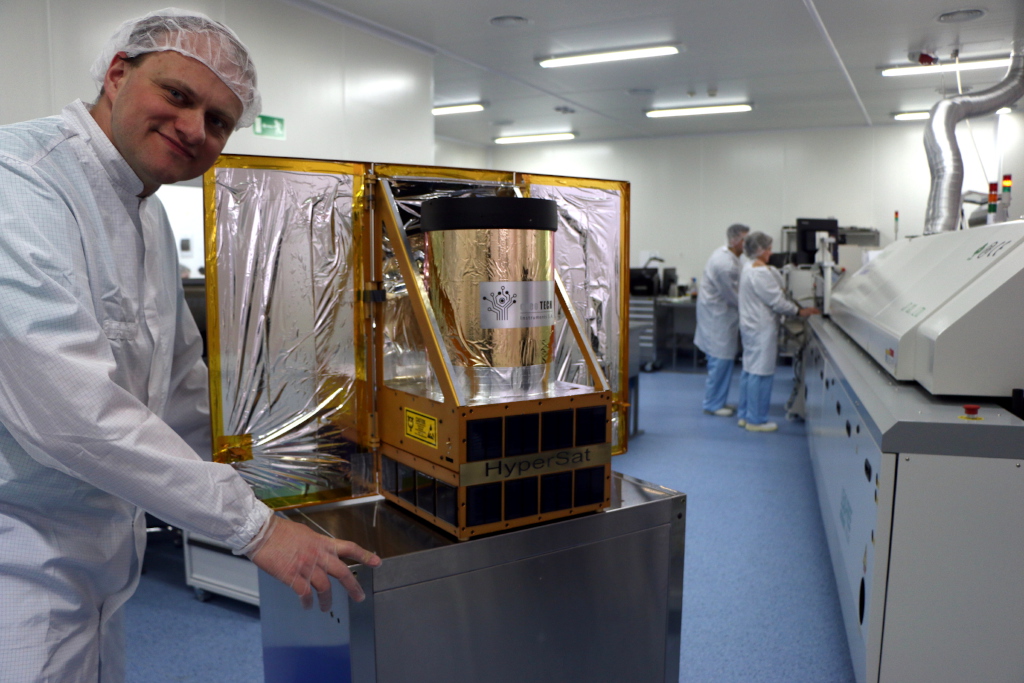

HyperSat is a modular, versatile satellite platform that, equipped with specialized instruments, will enable a broad spectrum of space missions, ranging from radar to telecommunication to optical ones. The HyperSat platform will benefit from the best practices of producing pico- and nanosatellites (called CubeSat), weighing several kilograms, but will be designed to carry larger instruments and apparatus. With its larger size, the use of HyperSat satellites will be significantly wider than that of nanosatellites. The Creotech product range will consist of replaceable functional modules. In the smallest configuration, the satellite will measure 30x30x10 cm and weigh 10 kg. The system can be expanded to a maximum size of 30x30x60 cm and a weight of 60 kg by adding additional modules or instruments. Within the Creotech project, a number of modular satellite subsystems will be developed and prepared for integration, including: a carrier structure capable of withstanding the congestion caused by a rocket flight and allowing the assembly of standardized components using the HyperSat BUS, such as a satellite-to-rocket separation subsystem, power subsystem and battery, photovoltaic panel subsystem, radio modulesand antennas.
Functions:
– R&D manager
2019 - Present
Rocket Electron at RocketLab

Functions:
– Senior RF Engineer
Copyright © Marcin Stolarski PhD. All rights reserved.
